Last Updated: 2 weeks ago by Gianna Porter
What Is eCommerce?
eCommerce, short for electronic commerce, refers to the buying and selling of goods and services over the Internet. It allows businesses and consumers to engage in online transactions without the need for a physical store. This industry has grown rapidly with the widespread use of the Internet, offering convenience and global reach for businesses of all sizes.
eCommerce Statistics
Understanding eCommerce statistics and forecasts is crucial for businesses to make informed decisions and strategies. It provides valuable insights into market trends, consumer behavior, and competitive landscapes. By knowing key metrics like sales growth, online shopping habits, emerging technologies, and popular products, businesses can adapt their offerings, marketing tactics, and operations to stay competitive in the ever-evolving eCommerce landscape.
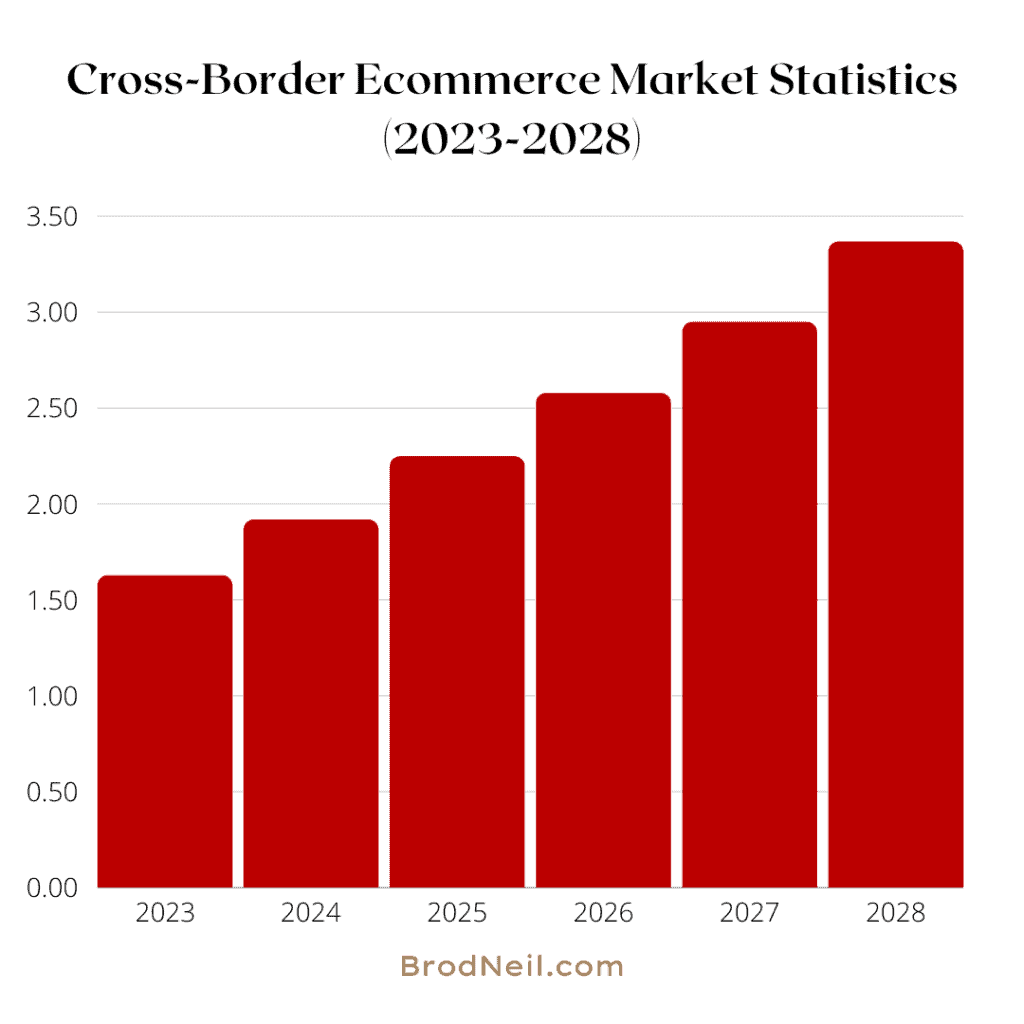
Cross-Border eCommerce Market Statistics (2023-2028)
What is cross-border eCommerce?
Cross-border eCommerce refers to online trading between businesses or consumers in different countries. It allows sellers to reach a global audience and buyers to access a wider range of products and services not available locally. Cross-border eCommerce involves navigating international regulations, logistics, payment methods, and customer preferences to facilitate seamless transactions across borders.
Below are the statistics and forecasts from 2023 to 2028.
Single-Vendor Vs Multi-Vendor eCommerce: Choosing the Right Model
With every passing day, the trend of online purchases is becoming common. People prefer buying products from an online multivendor marketplace rather than physically going out for shopping. This has become a powerful tool for various multivendor eCommerce platforms to perform better and make huge profits.
Today, you will see a lot of brands switching to hybrid stores i.e.; you can purchase both physically and online from such brands.
In the following article, we will help you better know the difference between a single-vendor platform & multivendor marketplace platform.
Single Vendor Model
A Single vendor model indicates one brand that has a website, where it sells its products. Different customers buy the product from a single vendor. This particular business model consists of two parties. These include the company and the customer. It is also known as the B2C marketing. On such a platform, you can advertise your products online so that people can purchase them while staying at home.
On a single-vendor marketplace, you sell your products without any third-party agent. It means you do not have to pay commissions to anyone for your sales. The overall revenue is yours.
Features of A Single Vendor Model
- Builds A Strong Relationship: The single vendor model consists of one seller who manages all the buyers because of this it helps to build a strong relationship with the customers
- Range of Products: Single vendor marketplace lets you list a limited range of stock
- Optimized workflow: A single-vendor model makes coordination, supply, and communications easier. Meanwhile, you are working from your company and are directly connected to the customers, it makes the communication clear and easy between you and the customer.
- Entry Into The Market: By using a single vendor model, individual sellers can easily enter the market, using their existing business knowledge. The transition to an online presence is all that they need!
- Products Managed By The Vendor: If the vendor has complete knowledge of the products including items that are sold out or no longer in demand, then it becomes easier to manage the customers and sales of the product.
Drawbacks
The single vendor management system offers its advantages, but it also brings along a specific set of drawbacks, including:
- Limited Product Variety: A single vendor model provides a limited range of products which is the biggest drawback of this model
- Dependency on a Single Source: It’s not easy for a single vendor to manage all the products of a brand. Any kind of disruption in the supply chain or at the side of the vendor can seriously impact all the operations of the business
- Scalability Challenges: Expanding the single vendor model requires effort and time and it can be very challenging if you have just started.
Multi-Vendor Model
A multivendor marketplace platform serves as an online mall that sells the products of different sellers. On this platform, several sellers come to sell their products under one roof. For instance, a shopping mall is the correct example of it. In it, different types of brands sell their products under one roof. Similarly, a multivendor market platform is a place where multiple sellers come, display their products, and sell their products with the help of a single administrator. Involving multiple sellers increases the potential for generating higher profit margins.
This model involves three entities: the vendor, the customer, and the admin, with the admin overseeing the platform where products are sold through aftership or aftership alternative..
Features of The Multi-Vendor Model
- Increased Variety of Products: This multivendor e-commerce platform increases the variety of products for selling under one roof. Having different brands, and different products means having multiple vendors. This way, it prevents dependency on a single vendor
- Centralized Administration: An admin centrally manages the overall marketplace including product listings and site functionality. That way, it ensures the formation of an organized and optimized marketplace
- Efficient Multivendor Management System: The Multi-Vendor model is considered the most powerful vendor management system (VMS), which optimizes, product updates, order processing, and performance tracking
- Scalability: The multivendor marketplace platform is easily scalable. Meanwhile, the platform can handle more visitors and transactions without slowing down
Drawbacks
Here are the drawbacks:
- Administrative Issues: It requires a smooth integration among various parties. Moreover, the involvement of multiple online interfaces is very challenging if any kind of issue arises with tasks and processes
- High Costs: This model is expensive compared to the single-vendor model
- Integration Issues: Integration becomes difficult as various teams handle the development and maintenance of different components
Conclusion
In the world of online business, deciding between a multivendor marketplace and a single-vendor marketplace is crucial for your business’s success. Whether you go for a diverse multivendor setup or a carefully curated single-vendor experience, having a strong vendor management system is vital for running your business successfully.